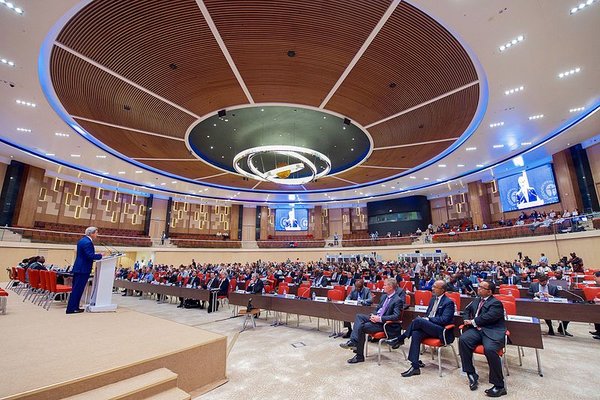
Negotiators from more than 170 countries on Saturday reached a legally binding accord to counter climate change by cutting the worldwide use of a powerful planet-warming chemical used in air-conditioners and refrigerators. The talks in Kigali, the capital of Rwanda, did not draw the same spotlight as the climate change accord forged in Paris last year. But the outcome could have an equal or even greater impact on efforts to slow the heating of the planet.
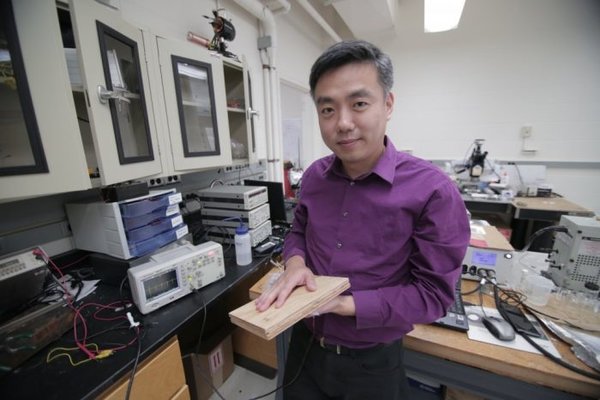
Continue reading... →Flooring can be made from any number of sustainable materials, making it, generally, an eco-friendly feature in homes and businesses alike. Now, however, flooring could be even more “green,” thanks to an inexpensive, simple method developed by University of Wisconsin–Madison materials engineers that allows them to convert footsteps into usable electricity. Wood pulp, which is already a common component of flooring, is partly made of cellulose nanofibers. They’re tiny fibers that, when chemically treated, produce an electrical charge when they come into contact with untreated nanofibers.
Continue reading... →NASA is funding projects with the potential to slash airplane greenhouse gas emissions by 75 percent. The agency is targeting airline emissions, a major source of greenhouse gases. NASA last week announced that it was funding research into five new technologies under a “green aviation” initiative that it says could cut airplane fuel use in half, reduce aircraft noise, and most important, slash carbon emissions by as much as 75 percent.
Continue reading... →At the recently concluded InnoTrans trade fair in Berlin, Germany unveiled the first ever hydrogen powered passenger train – a zero emission wonder that will be in operation from Dec 2017 and on-wards. Developed by the French company, Alstom, the ‘Coradia iLint’ train created quite a green stir in the world. Switching public transport to greener, more sustainable modes is on the agenda of most nations. And Germany seems to have flagged off this carbon free passenger train with great aplomb.
Continue reading... →On an expedition to the Ecuadorian rainforest, Yale students discovered a new type of fungus which may speed up the decomposition process of discarded plastics in landfills. Currently, Americans discard about 33.6 million tons of plastic each year. Only 6.5 percent of it is recycled and 7.7 percent is combusted in waste-to-energy facilities, which create electricity or heat from garbage. In result, there is a massive amount of non-biodegradable materials being tossed into landfills with a wait of about 1,000 years or so before they decompose. What’s worse, many of these materials may leak pollutants into the soil and water. The fungus is the first one that is known to survive on polyurethane alone, and it can do so in an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment, suggesting it could be used at the bottom of landfills.
Continue reading... →A monumental new biotechnology agreement between IKEA Supply AG and Newlight Technologies will signal another move away from unsustainable virgin fossil-based plastics in line with IKEA’s sustainability goals. The latest agreement will see IKEA invest in a 10 billion pounds production licence with Newlight sustainable materials. IKEA now has the exclusive rights in the home furnishings industry to use Newlight’s exciting carbon capture technology to convert bio-based greenhouse gases, from biogas and later from carbon dioxide, into AirCarbon thermoplastics for use in its range of home furnishing products.
Continue reading... →A group of scientists joined forces to craft a kind of living battery, which they call a bionic leaf for its melding of biology and technology. The device uses solar electricity from a photovoltaic panel to power the chemistry that splits water into oxygen and hydrogen. This bionic leaf converts CO2 in the air into alcohol that can be burned as fuel.
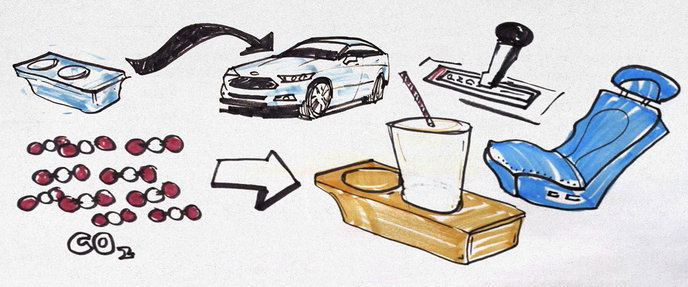
Continue reading... →One of the first companies to start making products out of carbon pollution is an automaker. For the last four years, Ford has been working with a manufacturer to develop a captured CO2-based foam, and soon a plastic, that can eventually replace parts made from petroleum.
Continue reading... →The salt-water powered car was recently approved in Europe. It works just like a hydrogen fuel cell except that the liquid used for storing energy is saltwater. This technology among others, are paving the way for clean green alternative fuel that have a serious potential to replace petroleum in many cases.
Continue reading... →