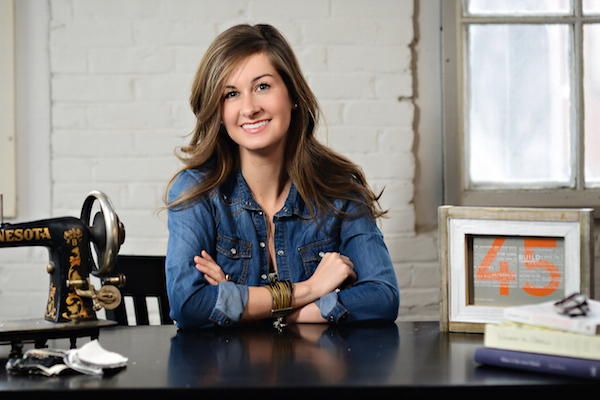
These women of the fashion world share their predictions of where the Eco-Fashion industry is headed in 2016. AMY HALL (DIRECTOR OF SOCIAL CONSCIOUSNESS, EILEEN FISHER) As an industry “insider,” I see three game-changing fashion trends taking deeper root in 2016. Fiber recycling: This is the year when we will find out which recycled-fiber developer will be the first to offer viable fabric suitable for mass-market apparel. So many are reaching for the golden ring. And it couldn’t come soon enough, what with deforestation and water scarcity threatening the future of virgin fibers as we know them. Living wage: After more than a century of stagnant wages for our garment-industry workers, there are murmurings of change on the horizon, such as the London living wage movement, the U.S. minimum wage campaigns, non-governmental organization activism, and brand acknowledgement of the severe impact that purchasing practices have on supply-chain compliance. Garment workers shouldn’t pop the champagne yet, but higher wages are in the air. Fast fashion: Nothing we do will really matter until we can loosen the consumers’ grip on “fast fashion” and get her to think of apparel as an investment. We repair our cars, our iPhones, and our furniture. Why […]
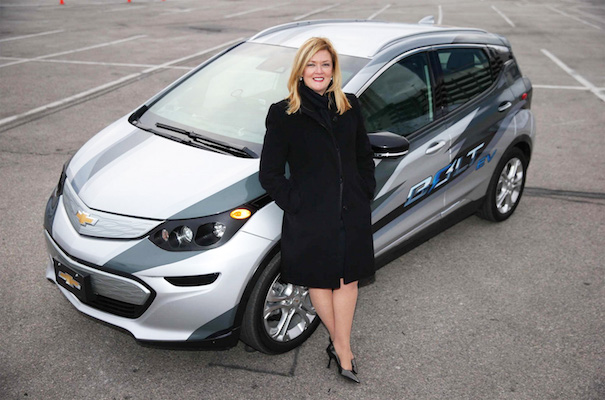
Continue reading... →GM turned heads at the 2016 CES (Consumer Electronics Show) with the launch of the groundbreaking 2017 Bolt electric vehicle, the first electric car with a long electric range (200 miles per charge, comparable to a Tesla Model S) but an affordable sticker price ($30,000). Inhabitat chatted with Pam Fletcher, the Executive Chief Engineer of Electric Vehicles over at GM to learn more about this accomplishment and what it took for one of the world’s largest car manufacturers to unveil such an innovative car. Read on for the interview. INHABITAT: Congratulations on the launch of the Chevy Bolt! How long did it take to get to that point? FLETCHER: The 2017 Chevrolet Bolt EV made its public debut yesterday after years of hard work. But one question that didn’t get a lot of attention in all the fanfare was: How did we get here? Many think our size is a disadvantage – that GM’s size is too big and not agile enough to develop a product like the Bolt EV. But without GM’s scale we would never have been able to build it and here’s why. It all starts with the people, and people is something GM has in abundance. […]
Continue reading... →With the end of the year just around the corner, we wanted to reflect on all that we have to be grateful for in 2015. There’s a lot to celebrate! From promoting conservation to empowering beginning farmers, here is the National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition’s list of the Top 15 Highlights of 2015: Conservation and Environment 1. 2015 opened with the first ever Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP) contract renewals. CSP, a program that NSAC has championed, is the only farm bill conservation program to support performance-based advanced conservation systems for working farms. 70 percent of expiring acres were renewed by producers ensuring that more than 17 million acres will continue to be supported through new and ongoing conservation activities. The year also ended on a high note for CSP: the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) postponed the CSP overhaul until 2017, buying more time for stakeholder input and outreach around the changes, and just this week Congress approved an omnibus budget bill that eliminated House-proposed cuts to CSP funding in 2016. 2. National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition (NSAC) member organizations and supporters submitted hundreds of comments to USDA recommending ways to improve the interim rules to implement 2014 Farm Bill changes to conservation programs, […]
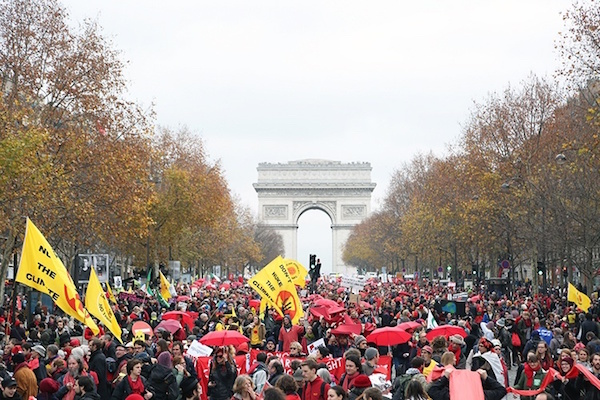
Continue reading... →Studies show that collective intelligence rises with the number of women in a group—but women are often underrepresented at talks like COP21. Meet 15 leaders worth listening to. Women, particularly those in developing countries, are on the frontlines of a changing climate. Extreme weather events, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity threaten their survival and that of their families. Yet, when confronted with social and economic exclusion, women’s vulnerabilities remain hidden and their voices quiet. Women have been severely underrepresented at high levels of policymaking around global environmental concerns as well. In the climate arena, the need to improve women’s participation in negotiations was explicitly recognized by COP 7 in Marrakech in 2001 as the impact of gender balance on decisionmaking became more evident. Why is this a problem? Studies show that collective intelligence rises with the number of women in a group. Engaging a critical mass of women is linked to more progressive and positive outcomes and to more sustainability-focused decisionmaking across sectors. Yet, women have remained a notable minority in climate negotiations at both the national and international level, in the global scientific body on climate change, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), and in media debates about climate. Women’s representation in bodies and […]
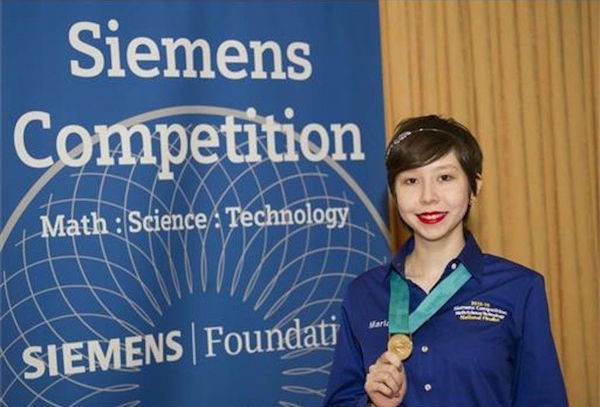
Continue reading... →17-year old Maria Elena Grimmett won the prestigious Siemens Competition in Math and Science for developing a new water purification method that can remove pharmaceutical pollutants from water. Maria Elena Grimmett was 11 when she noticed that her family’s well water was tinged brown, and she wondered why. Her curiosity sparked a six-year investigation into a new way to solve a common water pollution problem, and on Tuesday, that inquiry — conducted largely at Grimmett’s dining room table — won her a prestigious prize for young researchers and a $100,000 college scholarship. “Oh my goodness. I can’t tell you how shocked I was,” Grimmett, now 17, said outside an auditorium at George Washington University, which hosted the final round of the 2015 Siemens Competition in Math, Science and Technology. Grimmett’s initial questions about the color of her family’s water led her to learn about pharmaceutical pollution in the Florida Everglades. She was disgusted, and she wanted to help solve the problem. “I couldn’t imagine how people were letting this happen,” she said. So she settled on figuring out a new way to remove sulfamethazine, a common veterinary antibiotic used in pigs and cows, from water. Sulfamethazine contamination is common in rural areas, she said, and is helping to create antibiotic-resistant bacteria […]
Continue reading... →We can eliminate the use of fossil fuels completely and quickly, if countries can just find the political will. In a few decades, the world could be powered by nothing but wind, water, and sunlight. That’s the conclusion of a new study released just before world leaders meeting in Paris to strike a climate deal. “These are basically plans showing it’s technically and economically feasible to change the energy infrastructure of all of these different countries,” says Mark Z. Jacobson, director of the Atmosphere/Energy Program at Stanford University, who worked with University of California colleagues to analyze energy roadmaps for 139 countries. The researchers crunched numbers to see how much energy each country would need by 2050—including electricity, transportation, heating and cooling, industry, and agriculture—and then calculated how renewable energy could cover those needs, where it could go, and how much it would cost. People who are trying to prevent this change would argue that it’s too expensive, or there’s just not enough power, or they try to say that it’s unreliable, that it will take too much land area or resources,” Jacobson says. “What this shows is that all these claims are mythical.” Renewable energy is already cheap and […]
Continue reading... →Climate change action can feel so overwhelming, especially when we hear news of natural disasters, politicians who don’t believe in global warming, and companies who keep putting their money into dirty energy. So you might conclude that your voice doesn’t really matter at all in the grand scheme of global climate action. Let me convince you otherwise. I recently met with legendary feminist Eva Cox and discussed why the global environmental movement is facing so many challenges. For her, the key issues were these: We’re too negative. Many environmental activists and organizations focus too strongly on the threats and issues associated with climate change, such as natural disasters and spiraling pollution. This negative information has the effect of scaring people off: they’d rather ignore the issue than address it because it just seems all too hard. Instead, activists need to show the community that climate action has positive effects that help everyone. This uplifting message is much more likely to make people want to do something, rather than just stick their head in the sand. We’re not connecting the dots. It’s easy to pretend that climate change exists in isolation, but in reality it is connected to politics, society, employment, […]
Continue reading... →–and the average American does that 17 times a year. Food waste is a staggering problem. In 2010, close to 133 billion pounds, or a little over $160 billion worth of food, wound up in U.S. landfills. Kai Olson-Sawyer, a senior research and policy analyst at GRACE Communications Foundation, an organization that highlights the relationship between food, water and energy resources explains, “The fact is that food waste is truly a waste to all humanity of every kind.” That’s because when you toss a rotten apple or a moldy container of leftovers, you’re not just throwing away the food, but all the resources that went into producing it. “It’s really important to understand where and how things are grown,” says Ruth Mathews, executive director of the Water Footprint Network, an organization founded in 2008 to advance sustainable water use. Water plays a major role in food production, and as a result, food waste translates to an enormous amount of water wastage. All foods have a water footprint, the direct and indirect water that goes into producing a certain food—although some footprints are larger than others. In general, meats tend to need the most water for production, primarily because of the amount of food […]
Continue reading... →